Many times referred to as “Rheumatism of the Rich” gout is associated with overindulgence in riches and wine which only a wealthy man can afford, but now the prevalence of gout seems to be increasing and not limited to kings and wealthy men. It is a painful and potentially disabling form of arthritis that has been recognized since ancient times
Gout is a disease characterized by abnormal metabolism of uric acid, resulting in an excess of uric acid in the tissues and blood. People with gout either produce too much uric acid or more commonly, their bodies have a problem removing it.
The possible consequences of this build-up of uric acid in the body include:
- Acute and chronic gouty arthritis
- Kidney stones
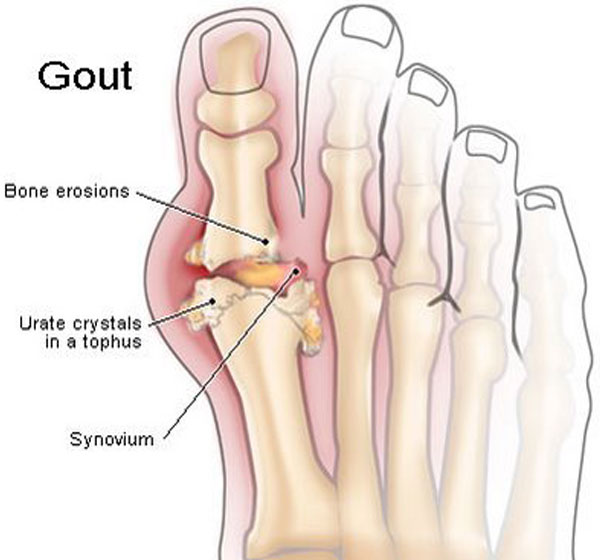
- Local deposits of uric acid (tophi) in the skin and other tissues.
Gout may occur alone (primary gout) or may be associated with other medical conditions or medications (secondary gout)
It is the most common cause of inflammatory arthritis in men over the age of 40
Causes of Gout
- Uric acid is generated as we metabolize the food we eat and as the body’s tissues are broken down during normal cell turnover.
- Gout occurs when excess uric acid (a normal waste product) accumulates in the body, and needle‐like crystals deposit in the joints.
- It also occurs often when the kidneys are unable to remove uric acid from the body adequately.
- A hereditary predisposition is also strongly indicated for a person to develop gout.
- Intake of alcoholic beverages, especially beer, and diets rich in red meats, internal organs, yeast, and oily fish increases the risk for gout.
- Prolonged use of certain medicines like chemotherapy drugs and immunosuppressants, diuretics, and anti-hypertensive compounds also trigger gout.
- Gout is strongly associated with obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes.
- The first symptom of gouty arthritis is typically the sudden onset of a hot, red, swollen joint with pains mostly appearing at night.
- The most common joint involved is at the base of the big toe where swelling is associated with severe tenderness. Apart from this, any joint can be involved (for example, the knee, ankle, and small joints of the hands).
- The acute pain is so intense that even the touch of the bed sheet is intolerable.
- While the first attacks usually involve only one or two joints, multiple joints are involved simultaneously over time.
- With time, attacks of gouty arthritis occur more frequently and last longer.
- Uric acid crystals also form outside small joints. Collections of these crystals, known as tophi are found in the earlobe, elbow, and Achilles tendon (back of the ankle), or in other smaller joints ultimately causing pain around the area.
Homeopathic treatment of Gout
- Homeopathic medicines have a long history of treating and curing gout.
- Apart from giving relief in swelling and pain the medicines aid in the digestion of the proteins, which cause the uric acid build-up thus nipping the bud before the complaint becomes chronic and recurring in nature.
- Acute remedies like Aconite and Colchicum immediately help the patient in relieving the traumatizing pain when administered in the right potency and doses.
- Homeopathic medicines can be a big boon for all those who suffer from high uric acid. These medicines work by reducing uric acid’s overproduction by the body and accelerating the removal of this waste product from the kidneys.
- Benzoic acid and Lycopodium are a few of the indicated medicines which are helpful in lowering the increased levels of uric acid.
- Berberis Vulgaris is the sure shot indicated medicine when gout is associated with kidney stones.
- Once under the wings of Homeopathy, the patient is free from relapses in case of Gout and High Uric acid diathesis especially if he or she takes care and precaution and brings a change in the diet and lifestyle.
Gout Prevention
If you are at risk for gout the following measures will help in controlling the advancement of the condition along with proper medication –
- Eat a low-cholesterol, low-fat diet.
- Avoid foods that are high in purines (the biochemical in foods that is metabolized into uric acid), including shellfish and red meats.
- Slowly lose weight as this lowers uric acid levels. Losing weight too rapidly occasionally precipitates gout attacks.
- Restrict your intake of alcohol, especially beer.
- Stay hydrated.
- Increase your intake of dairy products, such as non-fat milk and yogurt, as they lower the frequency of gout attacks.